-
Platform
BackManage PKI and Certificate Risk in One PlaceManage PKI and Certificate Risk in One PlaceThe Smarter Way to Manage Certificate LifecyclesContinuous Signing for CI/CD & DevOpsSecure, Flexible and Global SigningTrusted From Silicon to In-the-FieldDevice Security Without CompromiseAccelerate Secure App Development

-
Solutions
BackThe Smarter Way to Manage Certificate LifecyclesSoftware Supply Chain Security
Protect your entire software supply chain with automated tools

-
Buy
BackWildcard DomainBUY
Find the right TLS/SSL Certificate to secure your website
eIDAS-compliant transaction and website document security solutions
-
Company
BackManage PKI and Certificate Risk in One PlaceManage PKI and Certificate Risk in One PlaceThe Smarter Way to Manage Certificate LifecyclesContinuous Signing for CI/CD & DevOpsSecure, Flexible and Global SigningTrusted From Silicon to In-the-FieldDevice Security Without CompromiseAccelerate Secure App Development

-
Resources
Back
-
Support
BackContact Our Support Team
- Americas
- 1.866.893.6565 (Toll-Free U.S. and Canada)
- 1.801.770.1701 (Sales)
- 1.801.701.9601 (Spanish)
- 1.800.579.2848 (Enterprise only)
- 1.801.769.0749 (Enterprise only)
- Europe, Middle East Africa
- +44.203.788.7741
- Asia Pacific, Japan
- 61.3.9674.5500
- Americas
- Contact us
- Language
Join the world’s top digital experts in the first global focus on preparing for the quantum computing revolution. Watch now >

ML-DSA
A Quantum Cryptography Solution for Digital Signing
Optional heading that can be visually hidden
What is ML-DSA
(CRYSTALS-Dilithium)?
Module-Lattice-Based Digital Signature Algorithm (ML-DSA) is lattice-based signing that protects against quantum computing threats. It is based on the CRYSTALS (Cryptographic Suite for Algebraic Lattices) family of Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) algorithms, and it is particularly well suited to protecting against chosen-message attacks. ML-DSA was known as CRYSTALS-Dilithium during development and testing. Dilithium was renamed ML-DSA after its approval as a NIST standard in 2024.
ML-DSA is considered a general-purpose digital signature scheme meant to replace RSA- and ECC-based digital signatures. Its performance is already on par with previous schemes and should only improve going forward. However, the signatures and public keys are significantly larger than the quantum-vulnerable counterparts, potentially creating resource issues that must be accounted for in systems design and deployment.

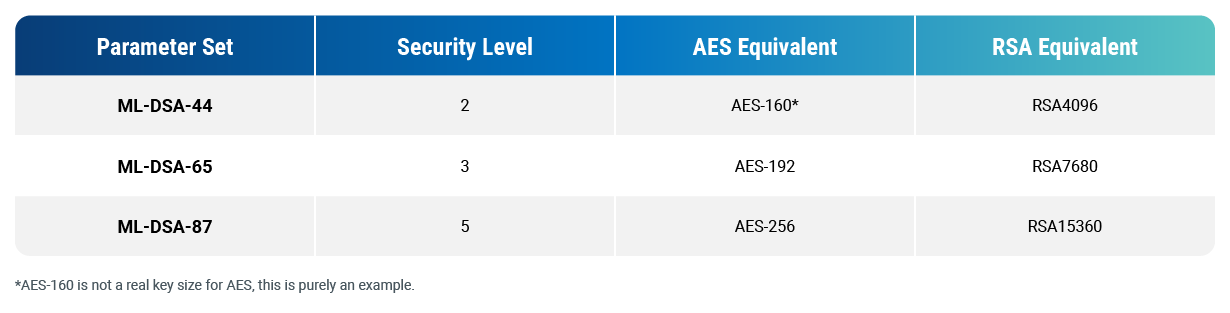
ML-DSA Parameter Sets
ML-DSA has three parameter sets
- ML-DSA-44
- ML-DSA-65
- ML-DSA-87
Each of the parameter sets corresponds to a security level. The security level, and the equivalent RSA scheme are:

ML-DSA by the Numbers
At its base, Dilithium operates on Lyubashevsky’s The most important consideration when using ML-DSA is whether the increase in size will work seamlessly with the protocol. Below is a list of the sizes of ML-DSA with comparisons with its RSA and ECC counterparts. RSA 2048 and Ed25519 are used as the comparison since they are the most widely utilized RSA and ECC signature schemes for certificates.





NIST Standardization
In August 2024, the United States National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) standardized ML-DSA in their FIPS 204 document. They assert that ML-DSA is usable by US government organizations for sensitive information.
Further, NIST has given guidance that organizations should switch from RSA and ECC to ML-DSA by 2030. They have also commented that after 2035, quantum-ready cryptography (also known as Post-Quantum Cryptography, or PQC) will be mandatory for government agencies.
-
Company
-
My Account
-
Resources
-
Sites
-
© 2025 DigiCert, Inc. All rights reserved.
Legal Repository Audits & Certifications Terms of Use Privacy Center Accessibility Cookie Settings


